Outside Air and ASHRAE 62.1 Analysis
Outside Air and ASHRAE 62.1 Analysis Report
The Outside Air / ASHRAE Standard 62.1 Summary is divided into six sections, and these six sections require fluency in ASHRAE 62.1 to properly understand. For more information on ASHRAE 62.1, please see the standard itself as well as the document titled “ASHRAE Standard 62.1: Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor Air Quality” in the Getting Started Guide.
A Glossary of Terms is at the end of this document.
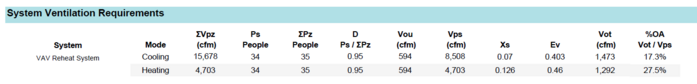
System Ventilation Requirements
The first table is titled “System Ventilation Requirements”. This table summarizes the values that are ultimately determining the outcomes. The user should pay close attention to the Xs and Ev values, as those values often explain differences between the standard and the user’s expectation. The Xs, Ev, and all other ASHRAE 62.1 variables for each zone are shown in the tables titled “Ventilation Calculations for Cooling Design” and “Ventilation Calculations for Heating Design”. If ventilation is not as expected, locate the zones matching the Xs and Ev values in the System Ventilation Requirements, then focus on those specific zones. In Single Zone systems, in zone direct dedicated outdoor air units, and in systems set to Sum of Outdoor Air, Ev will equal Ez. This is not a complete list and there are exceptions somewhere.
The definitions of the many terms in this process are established by the ASHRAE 62.1 standard. See the Glossary of Terms at the end of this document.
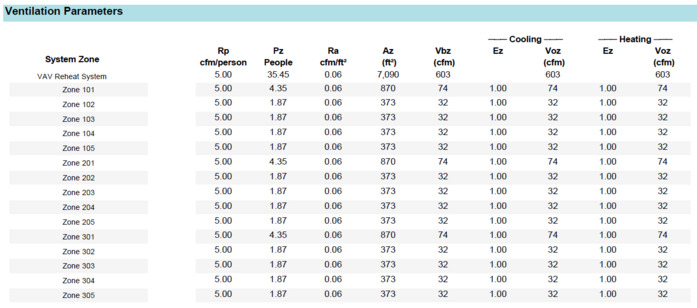
Ventilation Parameters
The second table is titled “Ventilation Parameters”. In this table are a summary of the people rates, area rates, and the Ez effectiveness values for heating and cooling. This calculation produces the Voz ventilation requirement for each zone prior to the ASHRAE 62.1 critical zone analysis. All terms are defined by ASHRAE 62.1. See the Glossary of Terms at the end of this document.
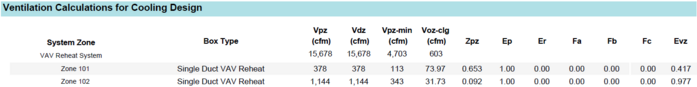
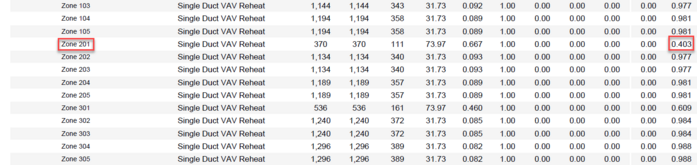
Ventilation Calculations for Cooling Design
The ASHRAE 62.1 calculations are performed for all zones in cooling mode. The user may read ASHRAE 62.1 for the details for all these parameters below. The main point of this table is Evz on the far right. The lowest Evz value is the driver for the entire system. Notice the 0.403 value for Zone 201. The value 0.403 is the system Ev in the System Ventilation Requirements table above, driving the outdoor air percentage of the main air handler. The typical solution to remove the harsh impact of Zone 201 would be to increase the minimum primary airflow of the zone, by either raising minimum stop, decreasing the heating supply air temperature, or increasing the cooling supply air temperature. The engineer must be aware of all requirements pertaining to their project before making such a change, however.
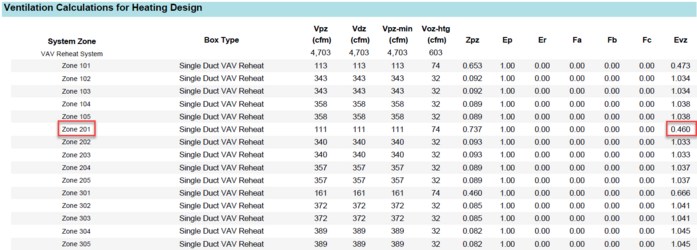
Ventilation Calculations for Heating Design
The ASHRAE 62.1 calculations are performed for all zones in heating mode. The user may read ASHRAE 62.1 for the details for all these parameters below. The main point of this table is Evz on the far right. The lowest Evz value is the driver for the entire system. Notice the 0.460 value for Zone 201. The value 0.460 is the system Ev in the System Ventilation Requirements table above, driving the outdoor air percentage of the main air handler. The typical solution to remove the harsh impact of Zone 201 would be to increase the minimum primary airflow of the zone, by either raising minimum stop, decreasing the heating supply air temperature, or increasing the cooling supply air temperature. The engineer must be aware of all requirements pertaining to their project before making such a change, however.
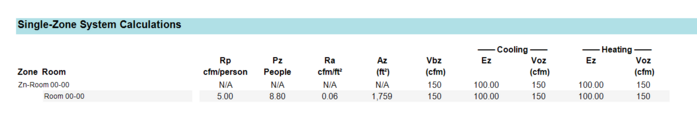
Single Zone System Calculations
This table will populate for single zone systems, where the math is less complicated than for multiple zone systems. The critical zone analysis in the multiple zone calculation does not apply to a single zone system.
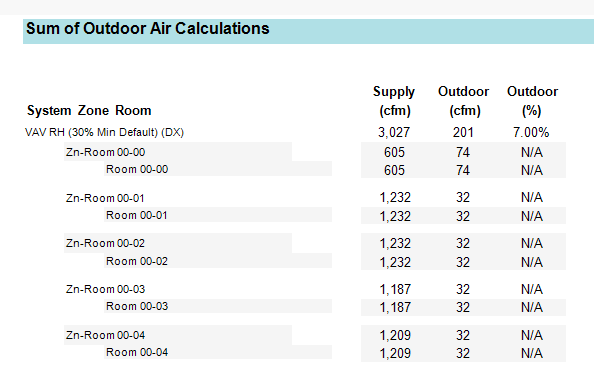
Sum of Outdoor Air Calculations
This table shows the ventilation without the ASHRAE 62.1 process applied. In Systems -> Configure Systems -> Properties -> Sizing, set the Ventilation Method to Zone Sum – Sum of Outdoor Air.

Glossary of Terms
All terms below are defined as written in ASHRAE 62.1-2016.
Az zone floor area: the net occupiable floor area of the ventilation zone, ft2 (m2).
D occupant diversity: the ratio of the system population to the sum of the zone populations
Ep primary air fraction: the fraction of primary air in the discharge air to the ventilation zone
Er secondary recirculation fraction: in systems with secondary recirculation of return air, the fraction of secondary recirculated air to the zone that is representative of average system return air rather than air directly recirculated from the zone.
Ev system ventilation efficiency: the efficiency with which the system distributes air from the outdoor air intake to the breathing zone in the ventilation-critical zone, which requires the largest fraction of outdoor air in the primary airstream. Ev shall be determined in accordance with Section 6.2.5.2 or Section A1.
Evz zone ventilation efficiency: the efficiency with which the system distributes air from the outdoor air intake to the breathing zone in any particular ventilation zone.
Ez zone air distribution effectiveness: a measure of the effectiveness of supply air distribution to the breathing zone. Ez is determined in accordance with
Fa supply air fraction: the fraction of supply air to the ventilation zone that includes sources of air from outside the zone.
Fb mixed-air fraction: the fraction of supply air to the ventilation zone from fully mixed primary air.
Fc outdoor air fraction: the fraction of outdoor air to the ventilation zone that includes sources of air from outside the zone.
Ps system population: the simultaneous number of occupants in the area served by the ventilation system.
Pz zone population: see Section 6.2.2.1.
Ra area outdoor air rate: see Section 6.2.2.1.
Rp people outdoor air rate: see Section 6.2.2.1.
Vbz breathing zone outdoor airflow: see Section 6.2.2.1.
Vdz zone discharge airflow: the expected discharge (supply) airflow to the zone that includes primary airflow and secondary recirculated airflow, cfm (L/s).
Vot outdoor air intake flow: see Sections 6.2.3, 6.2.4, and 6.2.5.4.
Vou uncorrected outdoor air intake: see Section 6.2.5.3.
Voz zone outdoor airflow: see Section 6.2.2.3.
Vps system primary airflow: the total primary airflow supplied to all zones served by the system from the air-handling unit at which the outdoor air intake is located.
Vpz zone primary airflow: see Section 6.2.5.1.
Xs average outdoor air fraction: at the primary air handler, the fraction of outdoor air intake flow in the system primary airflow.
Zpz primary outdoor air fraction: the outdoor air fraction required in the primary air supplied to the ventilation zone prior to the introduction of any secondary recirculation air.
%OA Vot/Vps Percent of outdoor air for the system.
D occupant diversity: the ratio of the system population to the sum of the zone populations
Ep primary air fraction: the fraction of primary air in the discharge air to the ventilation zone
Er secondary recirculation fraction: in systems with secondary recirculation of return air, the fraction of secondary recirculated air to the zone that is representative of average system return air rather than air directly recirculated from the zone.
Ev system ventilation efficiency: the efficiency with which the system distributes air from the outdoor air intake to the breathing zone in the ventilation-critical zone, which requires the largest fraction of outdoor air in the primary airstream. Ev shall be determined in accordance with Section 6.2.5.2 or Section A1.
Evz zone ventilation efficiency: the efficiency with which the system distributes air from the outdoor air intake to the breathing zone in any particular ventilation zone.
Ez zone air distribution effectiveness: a measure of the effectiveness of supply air distribution to the breathing zone. Ez is determined in accordance with
Fa supply air fraction: the fraction of supply air to the ventilation zone that includes sources of air from outside the zone.
Fb mixed-air fraction: the fraction of supply air to the ventilation zone from fully mixed primary air.
Fc outdoor air fraction: the fraction of outdoor air to the ventilation zone that includes sources of air from outside the zone.
Ps system population: the simultaneous number of occupants in the area served by the ventilation system.
Pz zone population: see Section 6.2.2.1.
Ra area outdoor air rate: see Section 6.2.2.1.
Rp people outdoor air rate: see Section 6.2.2.1.
Vbz breathing zone outdoor airflow: see Section 6.2.2.1.
Vdz zone discharge airflow: the expected discharge (supply) airflow to the zone that includes primary airflow and secondary recirculated airflow, cfm (L/s).
Vot outdoor air intake flow: see Sections 6.2.3, 6.2.4, and 6.2.5.4.
Vou uncorrected outdoor air intake: see Section 6.2.5.3.
Voz zone outdoor airflow: see Section 6.2.2.3.
Vps system primary airflow: the total primary airflow supplied to all zones served by the system from the air-handling unit at which the outdoor air intake is located.
Vpz zone primary airflow: see Section 6.2.5.1.
Xs average outdoor air fraction: at the primary air handler, the fraction of outdoor air intake flow in the system primary airflow.
Zpz primary outdoor air fraction: the outdoor air fraction required in the primary air supplied to the ventilation zone prior to the introduction of any secondary recirculation air.
%OA Vot/Vps Percent of outdoor air for the system.