Glazing Constructions Properties
Glazing Constructions Calculated Values
Constructions calculate the following values based on the layers of materials they have:
Outside and Inside surface convective heat transfer coefficient
Since they are calculated during the EnergyPlus™ simulation, outside and inside air film resistances are never allowed as a layer within a construction library member. In order to display approximated values in the library, outside and inside surface convective heat transfer coefficients have been taken from ASHRAE 90.1-2004 Normative Appendix A. Note that these are only approximations; actual calculated values will be available after calculation.
|
Default value:
|
value taken from ASHRAE 90.1-2013, Appendix A for appropriate surface type
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 < x <= 100,000
|
|
Typical Range:
|
0-150
|
|
Units:
|
(m2K)/W; (ft2•°F•hr)/Btu
|
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient
This field describes the value for SHGC, or solar heat gain coefficient. There are no units. This is the rated (NFRC) value for SHGC under summer cooling conditions and represents SHGC for normal incidence and vertical orientation.
|
Default value:
|
calculated
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 < x <= 100,000
|
|
Typical Range:
|
0.2-1.5
|
|
Units:
|
N/A
|
Direct Solar Transmission
This is the transmittance at normal incidence averaged over the solar spectrum.
Visible transmittance
This is the transmittance normal incidence averaged over the solar spectrum and weighted by the response of the human eye.
U-Factor (ASHRAE calculation)
This field describes the U-Factor or overall heat transfer coefficient. This is the rated (NFRC) value for U-factor under winter heating conditions. The U-factor is assumed to be for vertically mounted products. Although the maximum allowable input is U-7.0 W/m2K, the effective upper limit of the glazing generated by the underlying model is around U-5.8 W/m2K.
|
Default value:
|
blank
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 < x <= 100,000
|
|
Typical Range:
|
1 to 7 W/m2K; 0.01 to 1.0 Btu/(hr•ft2•°F)
|
|
Units:
|
W/m2K; Btu/(hr•ft2•°F)
|
Internal Shading Control Options
Internal shading control options allow you to specify the type and location of the shading device, what variable or combination of variables control deployment of the shading device, and what the control set point is. If the shading device is a blind, you also specify how the slat angle is controlled.
As shown in the figure below, a shading device can be inside the window, outside the window, or between panes of glass. The exception is window screens which can only be outside the window. When a shading device is present it is either retracted or activated. When it is retracted it covers none of the window. When it is activated, it covers the entire glazed part of the window (but not the frame). To model a case in which the shading device, when activated, covers only part of the window you will have to divide the window into two separate windows, one with the shading device and one without the shading device.
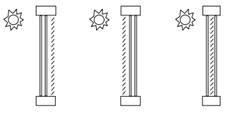
The internal control options for the three types of internal shading devices are:
Location of device
The choices are: “Inside window”, “Outside window” and “Between glass”. Note that the “Between Glass” option is not available if the default material in the glazing layer tab is a simple glazing material.
Type of slat angle control for blinds
This field is only valid for blinds and specifies how the slat angle is controlled. The choices are “Fixed angle”, “Scheduled” and “Block solar beams”. If “Fixed angle” (the default) is selected, the angle of the slat is fixed at the value input for the blind in the materials library. If “Scheduled” is selected, the slat angle varies according to the schedule specified below. If option is “Block solar beams”, the slat angle is set each time step to just block beam solar radiation. If there is no beam solar on the window the slat angle is set to the value input for the blind in the materials library. The “Block solar beams” option prevents beam solar from entering the window and causing possible unwanted glare if the beam falls on work surfaces while at the same time allowing near-optimal indirect radiation for daylighting.
Schedule for slat angle
This field is only valid for blinds and it defines the schedule that will vary the slat angle of the blinds. Make sure that the schedule values fall within the range given by the Minimum Slat Angle and Maximum Slat Angle values entered in the corresponding blind material. If not, the program will force them into this range. See Schedules for more information on creating schedules.
Shading control type
Specifies how the shading device is controlled, i.e., it determines whether the shading device is “on” or “off.” For blinds, screens and shades, when the device is “on” it is assumed to cover all of the window except its frame; when the device is “off” it is assumed to cover none of the window (whether “on” or “off” the shading device is assumed to cover none of the wall that the window is on).
The control type options are:
Always on - Shading is always on.
Always off - Shading is always off.
On if schedule allows - Shading is on if schedule value is non-zero. It requires that a schedule name be specified.
Note: For exterior windows with screens, "Always on", "Always off" and "On if schedule allows" are the only valid shading control types.
The following six control types are used primarily to reduce zone cooling load due to window solar gain:
On if solar radiation exceeds set point - Shading is on if beam plus diffuse solar radiation incident on the window exceeds the specified set point (W/m2) and the schedule, if specified, allows shading.
On if horizontal radiation exceeds set point - Shading is on if total (beam plus diffuse) horizontal solar irradiance exceeds set point (W/m2) and the schedule, if specified, allows shading.
On if OA temperature exceeds set point - Shading is on if outside air temperature exceeds set point (C) and the schedule, if specified, allows shading.
On if zone exceeds temperature set point - Shading is on if zone air temperature in the previous time step exceeds set point (C) and schedule, if specified, allows shading.
On if zone load exceeds set point - Shading is on if zone cooling rate in the previous time step exceeds set point (W) and schedule, if specified, allows shading.
On if daylighting glare index exceeds set point - Shading is on if the total daylight glare index at the zone’s first daylighting reference point from all of the exterior windows in the zone exceeds the maximum glare index specified in the daylighting input for zone (see Daylighting). It is applicable only to windows in zones with daylighting. Note: Unlike other Shading Control Types, glare control is active whether or not a schedule is specified.
The following three control types can be used to reduce zone heating load during the winter. This is done by by reducing window conductive heat loss at night and leaving the window unshaded during the day to maximize solar gain. They are applicable to any Shading Type except Exterior Screen but are most appropriate for interior or exterior shades with high insulating value ("movable insulation"). “Night” means the sun is down and “day” means the sun is up.
On at night if OA is below set point - Shading is on at night if the outside air temperature is less than set point (C) and the schedule, if specified, allows shading. Shading is off during the day.
On at night if zone temperature is below set point - Shading is on at night if the zone air temperature in the previous time step is less than set point (C) and schedule, if specified, allows shading. Shading is off during the day.
On at night if zone heating load exceeds set point - Shading is on at night if the zone heating rate in the previous time step exceeds set point (W) and the schedule, if specified, allows shading. Shading is off during the day.
The following two control types can be used to reduce zone heating and cooling load. They are applicable to any Shading Type except Exterior Screen but are most appropriate for translucent interior or exterior shades with high insulating value ("translucent movable insulation").
On during the day if zone load is not zero and on at night if OA temperature is less than set point - Shading is on at night if the outside air temperature is less than set point (C). Shading is on during the day if the zone cooling rate in the previous time step is non-zero. Night and day shading is subject to schedule, if specified.
On during the day if cooling load is not zero and on at night if the zone heating load exceeds set point - Shading is on at night if the zone heating rate in the previous time step exceeds set point (W). Shading is on during the day if the zone cooling rate in the previous time step is non-zero. Night and day shading is subject to schedule, if specified.
The following control types can be used to reduce zone cooling load. They are applicable to any Shading Type except Exterior Screen but are most appropriate for interior or exterior blinds, interior or exterior shades with low insulating value, or switchable glazing.
On during the day if solar radiation exceeds set point and zone cooling load is not zero - Shading is off at night. Shading is on during the day if the solar radiation incident on the window exceeds set point (W/m2) and if the zone cooling rate in the previous time step is non-zero. Daytime shading is subject to schedule, if specified
On at night and during the day if solar radiation exceeds set point plus cooling load is not zero - Shading is on at night. Shading is on during the day if the solar radiation incident on the window exceeds set point (W/m2) and if the zone cooling rate in the previous time step is non-zero. Day and night shading is subject to schedule, if specified. (This Shading Control Type is the same as the previous one, except the shading is on at night rather than off.)
On if OA temperature exceeds set point and if solar radiation exceeds set point - Shading is on if the outside air temperature exceeds the set point (C) and if the solar radiation incident on the window exceeds set point 2 (W/m2).
Is shading scheduled?
Select Yes or No. If yes, then schedule name must be selected in next field.
Schedule
Specify the name of the schedule to apply for the shading control. If Schedule Name is not specified, shading control is assumed to be active at all times. See Schedules for more information on creating schedules.
Activate glare control
Accepts values Yes and No. The default is NO. If Yes and the window is in a daylit zone, shading will be on if the zone's discomfort glare index exceeds the maximum discomfort glare index specified in the Daylighting object referenced by the zone.
Activation set point for control
This is the set point for activating window shading. The units depend on the type of trigger: W/m2 for solar-based controls, W for cooling- or heating-based controls, and Degrees °C for temperature-based controls. Setpoint is unused for shading control types “On if schedule allows” and “On if daylighting glare index exceeds set point”.
Second set point
Used only for control types that require two set points.
Storm Window Properties
As shown in the image below, a storm window is an extra layer of glass that is placed on an external glass door or window during winter months to reduce heat loss. The required fields are:
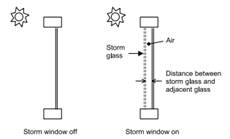
Distance between storm glass and window
This is the separation between the storm glass and the rest of the window, see figure above. It is measured from the inside of the storm glass layer to the outside of the adjacent glass layer.
Month and day that storm glass is put on window
It is assumed that the storm window is put in place at the beginning of this day, i.e., during the first simulation time step of the day.
Month and day that storm glass is taken off window
This is the day and month that the storm window is removed. It is assumed that the storm window is removed at the beginning of this day, i.e., during the first simulation time step of the day.
Between Glass Airflow Properties
Airflow source
This is the source of the gap airflow. The choices are:
-
Indoor Air - Indoor air from the window’s zone is passed through the window.
-
Outdoor Air - Outdoor air is passed through the window.
Airflow destination
This is where the gap air goes after passing through the window. The choices are:
-
Indoor Air - The gap air goes to the indoor air of the window’s zone.
-
Outdoor Air - The gap air goes to the outside air.
-
Return Air - the gap air goes to the return air for the window’s zone. This choice is allowed only if the Airflow Source is Inside Air. If the return air flow is zero, the gap air goes to the indoor air of the window’s zone. If the sum of the gap airflow for all of the windows in a zone set to Return Air exceeds the return airflow, then the difference between this sum and the return airflow goes to the indoor air.
The figure below shows the allowed combinations of Airflow source and Airflow destination. The allowed combinations are: Indoor Air -> Outdoor Air; Indoor Air -> Indoor Air; Indoor Air -> Return Air; Outdoor Air -> Indoor Air; Outdoor Air -> Outdoor Air.
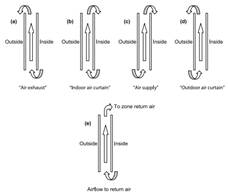
Maximum flow rate
This is the maximum value of the airflow, in m3/s per m of glazing width. The airflow can be modulated by specifying a schedule in the following field. The fan energy used to move the air through the gap is generally very small and so is ignored.
|
Default value:
|
blank
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 < x < 100,000
|
|
Typical Range:
|
0.006 to 0.009 m3/s•m; 4 to 6 cfm/ft
|
|
Units:
|
m3/s•m; ft3/min•ft
|
Control type
Specifies how the airflow is controlled. The choices are:
-
Always On At Maximum Flow - The airflow is always equal to Maximum Airflow.
-
Always Off - The airflow is always zero.
-
Scheduled Only - The airflow in a particular time step equals Maximum Airflow multiplied by the value of the Airflow Multiplier Schedule for that time step.
Schedule
This is the name of a utilization schedule with values between 0 and 100 percent. The time step value of the airflow is Maximum Airflow times the schedule value. See Schedules for more information on creating schedules.