Temperature
The temperature controller is used to control the temperature at a certain point in the supply air path. The temperature controller is required and there should be a temperature controller connected to each coil in the system. The location of the temperature controller determines at which point in the system the temperature will be controlled.
Note: The supply air temperature reset mentioned in several of these control strategies can also be called “supply air reset” and “outdoor air reset”.
|
|
Temperature Setpoint
The supply temperature is controlled to a certain constant temperature or variable temperature as defined in either the constant or variable control setpoint fields.
Setpoint Control Type: This defines if the supply air temperature setpoint will be a constant value or a variable value.
Constant Control Setpoint: This is the supply air temperature setpoint if the setpoint is constant.
Variable Control Setpoint: This is the supply air temperature setpoint if the setpoint is variable.
Supply air temperature reset per OA
The temperature at the location where this temperature controller is placed is controlled based on the outdoor air temperature. The SA temperature varies between a high SA temp and a low SA temp. When the OA temp is above a maximum value, the SA temperature will be equal to the high SA temp. When the OA temp is below a minimum value, the SA temperature will be equal to the low SA temp. When the OA is between the maximum and minimum value, the SA temperature will vary proportionally between the high and low SA temps.
Use system default: This will use a default outside air temperature reset based on the system that has been selected.
Outdoor air reset: A schedule can be applied to define the supply air and outdoor air temperature settings. This is an outdoor air reset schedule that defines the low and high outdoor air temperature set points.
Supply air reset per OA and worst case zone
The program will scan all of the zones assigned to this system to find the highest supply air dry bulb necessary to meet the worst case room sensible cooling load. The supply air dry bulb is not allowed to exceed SADBCPerOaReset + MaxResetTD.
Use system default: During the system simulation, the hourly supply air dry bulb will follow the default OA reset schedule for that system type.
Maximum reset: This is a temperature difference. The supply air temperature will be allowed to reset upwards by the temperature difference entered in this field.
Outdoor air reset schedule: The schedule defines when supply air reset will be allowed to be used.
Supply air reset per temp or airflow
The cooling supply air temperature will be reset in order to satisfy the warmest zone on the system.
Minimum supply air temperature: This is the minimum allowed supply air temperature. If the supply air temperature is calculated to be lower than this value, it will be reset to this value.
Maximum supply air temperature: This is the maximum allowed supply air temperature. If the supply air temperature is calculated to be greater than this value, it will be reset to this value.
Minimum turndown ratio: This is a fraction of the minimum allowable supply airflow to the maximum supply airflow. The decreased airflow can be achieved by either closing a VAV damper or decreasing the airflow through the supply fan.
Strategy - Control Based on Temperature: This controls to supply the highest supply air temperature at a minimum supply air flow rate that will satisfy all the zones on the system. As the loads increase, the supply airflow will increase. This will use less fan energy but more reheat energy.
Control Based on Flow: This controls to supply the highest supply air flow at a maximum supply air temperature that will satisfy all the zones on the system. As the loads increase, the supply air temperature will decrease. This will use more fan energy but less reheat energy.
Single zone control per control zone
This control method is used for a single zone variable temperature reheat system. The SA temperature is set to satisfy a particular control zone.
Each zone assigned to this system using this control strategy will be given its own set of coils. For example, if 10 zones are assigned to an individual Single Zone CV system, 10 systems will be created, one per zone.
Control zone: This will be the zone that the system will control the supply air temperature to. The control zones can only be selected in the project after zones have been assigned to the system. Note, in the project this field will be shown even before zones have been assigned but cannot be edited until after zones have been assigned to the system. By default, the first zone assigned to the system will be set as the control zone but any zone assigned to the system can be selected from this dropdown.
Minimum supply air temperature: This is the minimum allowable supply air temperature for the system.
Maximum supply air temperature: This is the maximum allowable supply air temperature for the system.
Supply air temperature reset per leaving component
The supply air temperature varies directly with the current temperature at a specific component outlet in the system.
Minimum supply air temperature: This is the minimum limit for the supply air temperature.
Maximum supply air temperature: This is the maximum limit for the supply air temperature.
Offset temperature difference: This is the temperature difference between the reference temperature and the supply air temperature. This value can be positive or negative.
Reference temperature type: The reference temperature can be either a dry bulb or a wet bulb temperature.
Reference component leaving temperature: The reference temperature will be the temperature at the outlet of the component defined in this field.
Supply air reset per single zone VAV
At maximum cooling load, the system supplies the minimum supply air temperature and maximum supply air flow. As the load decreases, the supply airflow decreases until it reaches a minimum value. At this point, the supply air temperature will begin to increase until the system switches into heating mode. As the heating load increases, the supply air temperature will continue to increase until it reaches a maximum value. At this point, the supply airflow will increase again until it reaches its maximum at the design heating load.
Each zone assigned to this system using this control strategy will be given its own set of coils. For example, if 10 zones are assigned to an individual Single Zone VAV system, 10 systems will be created, one per zone.
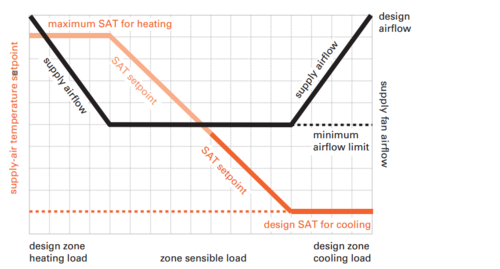
Fan control: There are three different methods that can be used to control the fan. The fan can be variable speed so it can operate at any speed within its range. The fan can operate at only two different speeds. The fan can also be set to it is variable volume when the system is in cooling mode but constant volume when the system is in heating mode.
Turndown ratio: This is a fraction of the minimum allowable supply airflow to the maximum supply airflow. The decreased airflow can be achieved by either closing a VAV damper or decreasing the airflow through the supply fan.
Maximum supply air temperature: This is the maximum limit for the supply air temperature.
Minimum supply air temperature: This is the minimum limit for the supply air temperature.
Enable fan static pressure modifier: This allows the fan static pressure to vary during the simulation.
Supply air temperature reset per main supply setpoint
This control strategy is only available for DOA systems. The conditioned outdoor air temperature from the DOA will be controlled to be equal to the main supply air temperature of the system it is associated with, even if the main system supply air temperature is being reset. For instance, if at a particular hour, the main system is being controlled to deliver 55 F air, the DOA will also be controlled to supply 55 F outdoor air.
Supply air temperature reset per mixed air condition
This control strategy is only available for DOA systems. The conditioned outdoor air temperature from the DOA will be controlled such that the mixed air temperature is equal to the main system supply air temperature. This is in an effort to prevent the main system coils from operating. For example, if the required SADB for a particular hour is 55 F, the system is 80% OA and the return air temperature is 75 F, the DOA should control the outdoor air to be conditioned to 50 F to cause the mixed air temperature to equal 55 F.
(% OA/100) * (T_OA) + (1 - (% OA/100)) * (T_RA) = T_MA
(0.8 * T_OA) + (0.2 * 75 F) = 55 F
T_OA = 50 F
Where % OA = percent of outdoor air
T_OA = outdoor air temperature after being conditioned by the DOA
T_RA = return air temperature
T_MA = mixed air temperature
Maximum Outdoor Air Temperature
This is the upper limit for the conditioned outdoor air temperature. If the calculated conditioned outdoor air temperature is higher than this value, the program will use this value.
Minimum Outdoor Air Temperature
This is the lower limit for the conditioned outdoor air temperature. If the calculated conditioned outdoor air temperature is lower than this value, the program will use this value.